08 Mar What Are Mebendazole’s?
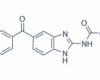
Mebendazole (MBZ), sometimes known as Vermox, is a medication used to treat parasitic worm infestations. Ascariasis, pinworm infection, hookworm infection, guinea worm infection, hydatid illness, and giardia are examples. It is taken by mouth.
Mebendazole is generally well tolerated. Common side effects include headache, vomiting, and ringing in the ears. When used in large doses, it may cause bone marrow suppression. It is uncertain if using it during pregnancy is safe. Mebendazole is an antihelminthic benzimidazole having a broad range of activity.
Mebendazole was first used in 1971, following its invention in Belgium by Janssen Pharmaceutica. It is on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines. Mebendazole is a generic medication.
Special-needs populations
Mebendazole has been shown in animal models to cause bad pregnancy outcomes, but no studies of its effects in human pregnancy have been conducted. It is unknown if it may be transferred through breastfeeding.
Medications and their interactions
Carbamazepine and phenytoin lower serum levels of mebendazole. Cimetidine has a limited systemic absorption and does not significantly enhance serum mebendazole levels (in contrast to the equivalent drug albendazole).
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and the more severe toxic epidermal necrolysis can occur when mebendazole is used with high doses of metronidazole.
Mechanism
Mebendazole suppresses microtubule formation by engaging with the colchicine binding area of -tubulin, inhibiting tubulin dimer polymerisation in parasite intestinal cells. The breakdown of cytoplasmic microtubules prevents the helminths from absorbing glucose and other nutrients, resulting in gradual immobilization and death.
Mebendazole’s limited digestive absorption makes it an efficient therapy for intestinal parasite infections with little adverse effects. Mebendazole, on the other hand, has an effect on mammalian cells, mostly through inhibiting the polymerization of tubulin dimers, resulting in the destruction of important microtubule structures such as the mitotic spindle. Apoptosis is caused by the collapse of the mitotic spindle, which is mediated by the dephosphorylation of Bcl-2, which allows the pro-apoptotic protein Bax to dimerize and promote programmed cell death.
Application in medicine
Mebendazole is a broad-spectrum antihelmintic that is used to treat nematode infestations such as roundworm, hookworm, whipworm, threadworm (pinworm), and the intestinal form of trichinosis before they spread into tissues outside of the digestive system. Because mebendazole is poorly absorbed into the bloodstream, different drugs are necessary to treat worm infections that have spread beyond the digestive tract. Mebendazole is used alone to treat mild to severe infestations. It slowly kills parasites and can cause some parasites to travel out of the digestive tract, resulting in appendicitis, bile duct difficulties, or intestinal perforation in individuals with significant infestations. Patients who are severely infected may be treated with piperazine before or instead of mebendazole to avoid this. Parasites are paralyzed by piperazine, allowing them to pass through the feces. On a rare occasion, it is used to treat cystic echinococcosis, also known as hydatid disease. However, there is little proof that this condition is effective.
Mebendazole and other benzimidazole antithelmetics are effective against nematode larvae and adults, as well as roundworm and whipworm eggs. Parasite lysis and death are time-consuming processes, and elimination in the feces may take several days.
Negative ramifications
Mebendazole may cause diarrhea, stomach pain, and elevated liver enzymes in certain persons. It has been related to dangerously low white blood cell counts, low platelet counts, and, in rare cases, hair loss, as well as the risk of agranulocytosis.
http://www.mhsvbrstudy.com/2020/01/10/fenbendazoles-history/
Research
Several studies have revealed that mebendazole has potent anticancer properties. Mebendazole significantly reduced cancer cell proliferation, migration, and metastatic growth of adrenocortical carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Mebendazole administration caused mitotic arrest in lung cancer cell lines, followed by apoptotic cell death with caspase activation and cytochrome c release. Mebendazole induced a dose- and time-dependent apoptotic response in human lung cancer cell lines, as well as apoptosis via Bcl-2 inactivation in chemoresistant melanoma cells. Mebendazole’s anti-cancer effect is supported by preclinical studies and case reports.